The phylogenetic distance between species often predicts differences in ecologically important traits. The phylogenetic diversity and structure of biological communities can inform our understanding of the processes that shape those communities, and there is a well‐developed framework for comparing phylogenetic structures of communities. However, particularly in studies of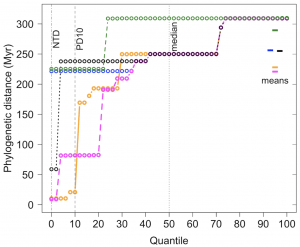 phylogenetic distances from one focal species to other members of its assemblage (a one‐to‐many framework), the standard metrics of community‐wide studies encounter significant limitations due to the left‐skewed distribution of pairwise phylogenetic distances in most biological communities. For studies that require estimating the degree of phylogenetic isolation of a focal taxon, the mean phylogenetic distance (MPD) usually provides little power to distinguish among taxa because it is heavily weighted by the many ways to be distantly related, whereas the nearest taxon distance (NTD) is highly idiosyncratic and ignores cases where multiple close relatives may contribute equally strongly to influence the focal species. Here we highlight the value of examining the cumulative distribution of phylogenetic distances in studies that take a focal‐species approach. We describe and discuss the benefits of two new metrics. An integrated metric of phylogenetic distances (AUPhyDC) uses information from the whole cumulative distribution, whereas the tenth quantile (PD10) is an extremely simple metric that improves on NTD by capturing the influence of multiple close relatives on ecological interactions. Several recent examples found that PD10 did a better job of revealing ecological patterns than NTD or MPD. We provide R code to facilitate the use of these approaches and advocate for the inclusion of PD10 along with NTD and MPD in statistical packages for phylogenetic ecology.
phylogenetic distances from one focal species to other members of its assemblage (a one‐to‐many framework), the standard metrics of community‐wide studies encounter significant limitations due to the left‐skewed distribution of pairwise phylogenetic distances in most biological communities. For studies that require estimating the degree of phylogenetic isolation of a focal taxon, the mean phylogenetic distance (MPD) usually provides little power to distinguish among taxa because it is heavily weighted by the many ways to be distantly related, whereas the nearest taxon distance (NTD) is highly idiosyncratic and ignores cases where multiple close relatives may contribute equally strongly to influence the focal species. Here we highlight the value of examining the cumulative distribution of phylogenetic distances in studies that take a focal‐species approach. We describe and discuss the benefits of two new metrics. An integrated metric of phylogenetic distances (AUPhyDC) uses information from the whole cumulative distribution, whereas the tenth quantile (PD10) is an extremely simple metric that improves on NTD by capturing the influence of multiple close relatives on ecological interactions. Several recent examples found that PD10 did a better job of revealing ecological patterns than NTD or MPD. We provide R code to facilitate the use of these approaches and advocate for the inclusion of PD10 along with NTD and MPD in statistical packages for phylogenetic ecology.
Gilbert, G. S. and I. M. Parker. 2022. Phylogenetic distance metrics for studies of focal species in communities: quantiles and cumulative curves. Diversity 14:521 https://doi.org/10.3390/d14070521